Scientists have discovered an unusually huge exoplanet. This is in orbit aroundb centauri‘, huge binary star systemIt can be seen with the naked eye.
With a total mass of about 10 sonn It is the heaviest known star system that has a planet and is in it 325 light years off the ground. From The study was published in the journal Nature, appears, this celestial body with the label “B Cen (AB) BMaybe a gas giant and heavier than that ten times Jupiter. So, one of the most massive planets ever discovered.
The orbit of an exoplanet is 100 times larger than that of Jupiter which is amazing. with more distance 83 billion km For host stars, this is one of the longest orbits ever recorded. For comparison: Pluto revolves around the Sun at a distance 5.3 billion km.
Discovery leads to rethinking
So far, no planets have been found in the orbit of stellar systems weighing more than three solar masses. Astronomers did not believe that planets could form around such systems. The discovery speaks to a fundamental questioning of previous theses about the architecture and educational conditions of the planets.
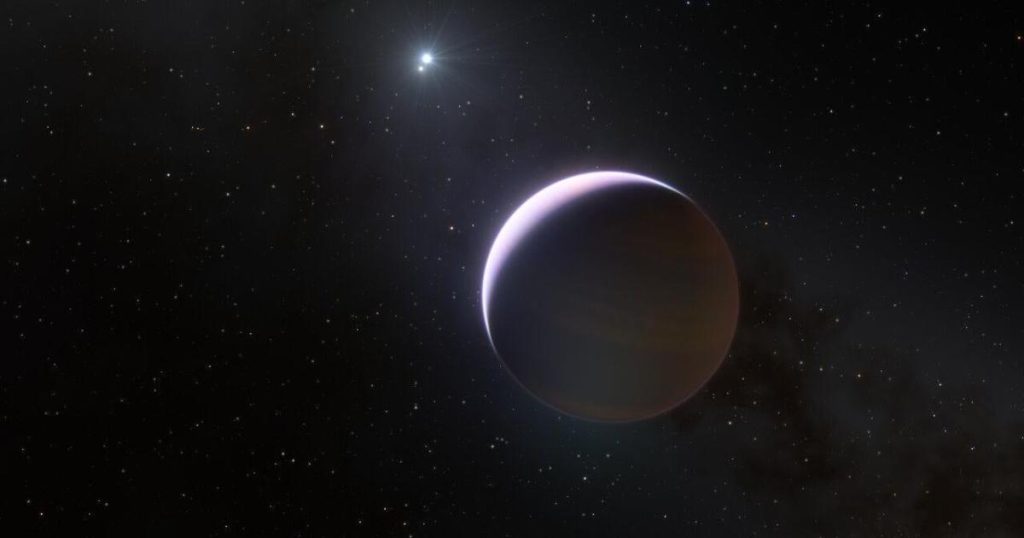
The B-Centauri system with the newly discovered exoplanet is shown here at the bottom right and the pair of stars on the left. The dot in the top right is an independent background star.
© ESO / Janson et al., 2021
Do you have young stars? protoplanetary discs around them, from which the planets eventually evolve. However, a hot star system like Centauri B is due to the massive amounts of it Ultraviolet and X-rays Not conducive to planet formation. by email wizmodo From Marcus Jansson, an astronomer at Stockholm University and first author of the study, this high-energy radiation tends to shut off the disks in a very short time destroy. It was previously assumed that this did not give the planet enough time to develop in the disk.
“It seems that no matter where we look — around small or large stars, single or double stars, living stars or the remnants of dead stars — we always find planets in some form, even in places we didn’t think were possible,” Janson said. It can be excluded that b Cen (AB) b is a brown dwarf. Janson explains that this will be hotter. Whether they are a new class of planets must be determined in fact using a larger sample of similar systems.
The team is currently conducting an investigation called Monster through, in 85 stars Scanned with similar characteristics. The result may shed light on how common this type of planet is and how it forms. According to Jason, the discovery of planet formation theorists will help refine their theories. It is hoped that the physical underpinnings that enable a wide range of planets to be observed around massive stars, sun-like stars, and small stars will be found.
Probably no life is possible
From an astrobiological standpoint, the exoplanet “is likely to be one of the worst places in the galaxy to harbor life,” according to Janson. The huge amount of UV and X-rays will affect any surface it is exposed to DisinfectHowever, Janson does not rule out the possibility of life in the subterranean oceans.
Janson and colleagues discovered Cen (AB) b with Sphere exoplanet imager A.m very large telescope The European Southern Observatory In Chile in the morning March 20, 2019 then again 10. April this year. To do this, the astronomers used a high-contrast imaging technique that enabled them to distinguish the weak light from the exoplanets from the very bright light from the star system itself. Follow-up studies have shown that the planet does exist 20 years ago by another ESO tool but it was not properly identified at the time.

“Total coffee aficionado. Travel buff. Music ninja. Bacon nerd. Beeraholic.”







More Stories
Study: Working full-time can affect your risk of cancer
The new “Karl” has arrived – Focus: Psychology
Psychology: 3 strategies to help when you can't concentrate